Physical backups and restores¶
Version added: 1.7.0
Implementation history
The following table lists the changes in the implementation of physical backups and the versions that introduced those changes:
| Version | Description |
|---|---|
| 2.0.0 | Physical backups and restores, physical restore with data-at-rest encryption |
| 2.3.0 | Physical backups in mixed deployments |
| 2.10.0 | Physical restore with a fallback directory |
Physical backup is copying of physical files from the Percona Server for MongoDB dbPath data directory to the remote backup storage. These files include data files, journal, index files, etc. Percona Backup for MongoDB also copies the WiredTiger storage options to the backup’s metadata.
Physical restore is the reverse process: pbm-agents shut down the mongod nodes, clean up the dbPath data directory and copy the physical files from the storage to it.
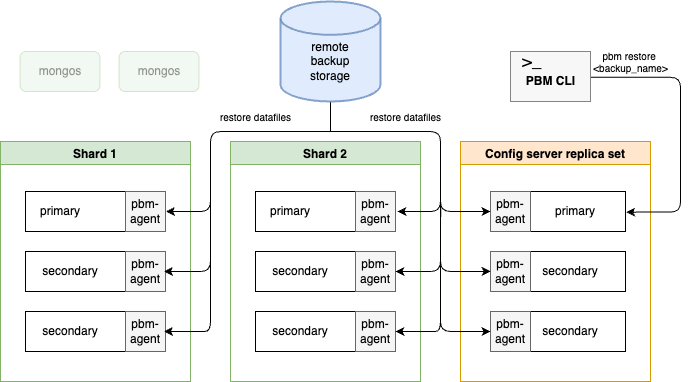
The following diagram shows the physical restore flow:
During the restore, the pbm-agents temporarily start the mongod nodes using the WiredTiger storage options retrieved from the backup’s metadata. The logs for these starts are saved to the pbm.restore.log file inside the dbPath. Upon successful restore, this file is deleted. However, it remains for debugging if the restore were to fail.
During physical backups and restores, pbm-agents don’t export / import data from / to the database. This significantly reduces the backup / restore time compared to logical ones and is the recommended backup method for big (multi-terabyte) databases.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| - Faster backup and restore speed - Recommended for big, multi-terabyte datasets - No database overhead |
- The backup size is bigger than for logical backups due to data fragmentation extra cost of keeping data and indexes in appropriate data structures - Extra manual operations are required after the restore - Point-in-time recovery requires manual operations |
Availability and system requirements¶
- Percona Server for MongoDB starting from versions 4.2.15-16, 4.4.6-8, 5.0 and higher.
- WiredTiger storage engine, since physical backups heavily rely on the WiredTiger
$backupCursorfunctionality.
Warning
During the period the backup cursor is open, database checkpoints can be created, but no checkpoints can be deleted. This may result in significant disk space growth during backup window. This should go back to normal after the backup cursor is closed.
See also
Percona Blog
Physical backup consists of copying the files from the Percona Server for MongoDB dbPath data directory to the remote backup storage. These files include data files, journal, index files, etc. Starting with version 2.0.0, Percona Backup for MongoDB also saves the WiredTiger storage options to the backup’s metadata.
Physical restore is the reverse process: each pbm-agent shuts down their local mongod node, cleans up the dbPath data directory and copies back the physical files from the backup storage location.
The following diagram shows the physical restore flow:
During the restore, the pbm-agents temporarily restart the mongod nodes two times using the WiredTiger storage options retrieved from the backup’s metadata. The logs for these starts are saved to the pbm.restore.log file inside the dbPath. Upon successful restore, this file is deleted. However, it is kept for debugging if the restore fails.
During physical backups and restores, pbm-agents don’t export / import data from / to the database. This significantly reduces the backup / restore time compared to logical ones and is the recommended backup method for big (> 100 GB) databases.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| - Faster backup and restore speed - Recommended for big, multi-terabyte datasets - No database overhead |
- The backup size is bigger than for logical backups due to data fragmentation extra cost of keeping data and indexes in appropriate data structures - Extra manual operations are required after the restore |
Make a backup Restore a backup
Physical backups in mixed deployments¶
Version added: 2.3.0
You may run both MongoDB Community / Enterprise Edition nodes and Percona Server for MongoDB (PSMDB) nodes in your environment, for example, when migrating to or evaluating PSMDB.
You can make a physical, incremental or a snapshot-based backup in such a mixed deployment using PBM. This saves you from having to reconfigure your deployment for a backup, and keeps both your migration and backup strategies intact.
Physical, incremental and snapshot-based backups are only possible from PSMDB nodes since their implementation is based on the $backupCursorExtend functionality. When it’s time to make a backup, PBM searches the PSMDB node and makes a backup from it. The PSMDB node must not be an arbiter nor a delayed node.
If more than 2 nodes are suitable for a backup, PBM selects the one with a higher priority. Note that if you override a priority for at least one node, PBM assigns priority 1.0 for the remaining nodes and uses the new priority list .
Consider the following flow for incremental backups:
By default, PBM picks the node from where it made the incremental base backup when it makes subsequent backups. PBM assigns priority 3.0 to this node ensuring that it is the first in the list. If you change the node priority, make a new incremental base backup to ensure data continuity.
The physical restore in mixed deployments has no restrictions except the versions in backup and in the source cluster must match.
Physical restores with data-at-rest encryption¶
Version added: 2.0.0
You can back up and restore data which is encrypted at rest. Thereby you ensure data safety and can also comply with security requirements such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, or PHI.
During a backup, Percona Backup for MongoDB stores the encryption settings in the backup metadata. You can verify them using the pbm describe-backup command. Note that the encryption key is not stored nor shown as part of the backup.
Important
Make sure that you know which master encryption key was used and keep it safe, as this key is required for the restore.
Note
Starting with Percona Server for MongoDB version 4.4.19-19 , 5.0.15-13 , 6.0.5-4 and higher, the master key rotation for data-at-rest encrypted with HashiCorp Vault has been improved to use the same secret key path on every server in your entire deployment. For the restore with earlier versions of Percona Server for MongoDB and PBM 2.0.5 and earlier, see the Restore for Percona Server for MongoDB before 4.4.19-19, 5.0.15-13, 6.0.5-4 using HashiCorpVault section.
To restore the encrypted data from the backup, configure the same data-at-rest encryption settings on all nodes of your destination cluster or replica set to match the settings of the original cluster where you made the backup.
During the restore, Percona Backup for MongoDB restores the data to all nodes using the same master key. We recommend to rotate the master encryption key afterwards for extra security.
To learn more about master key rotation, refer to the following documentation:
Restore for Percona Server for MongoDB before 4.4.19-19, 5.0.15-13, 6.0.5-4 using HashiCorpVault¶
In Percona Server for MongoDB version before 4.4.19-19, 5.0.15-13, 6.0.5-4 with Vault server used for data-at-rest encryption, the master key rotation with the same key used for 2+ nodes is not supported. If you run these versions of Percona Server for MongoDB and PBM before 2.1.0, consider using the scenario where PBM restores the data on one node of every replica set. The remaining nodes receive the data during the initial sync.
Configure data-at-rest encryption on one node of every shard in your destination cluster or a replica set.
During the restore, Percona Backup for MongoDB restores the data on the node where the encryption key matches the one with which the backed up data was encrypted. The other nodes are not restored, so the restore has the “partlyDone” status. You can start this node and initiate the replica set. The remaining nodes receive the data as the result of the initial sync from the restored node.
Physical restores with a fallback directory¶
Version added: 2.10.0
An unexpected error may occur during the physical restore phase, such as corrupted backup data files, network issues accessing backup storage or unexpected pbm-agent failures. When this happens, the files in the dbPath may be left in an inconsistent state and the affected mongod instance cannot be restarted. As a result, a replica set or shard in the cluster become non-operational. PBM becomes non-functional too, since it relies on MongoDB as both a communication channel and a metadata store.
To prevent this nasty situation, you can configure PBM to use a fallback directory and revert the cluster to its original state if errors occur during a physical restore. PBM copies the dbPath contents to the fallback directory at the restore start. Then the restore flows as usual.
If the restore is successful, PBM deletes the fallback directory and its contents.
If PBM detects that the cluster is in an error state, it automatically triggers the fallback procedure. PBM cleans up the uploaded backup files from the dbPath and moves the files from a fallback directory there. This way a cluster returns to the state before the restore and is operational. You can then retry the same restore or try restoring from a different backup.
Warning
Note that this functionality comes with a tradeoff: you must have enough disk space on every mongod instance to copy the contents of the dbPath to a fallback directory. For this reason, fallback directory usage is disabled by default. Read more about disk space requirements in the Disk space evaluation section.
Disk space evaluation¶
Each mongod node must have enough free space for PBM to copy the contents of the dbPath into the fallback directory. In addition, at least 15% of total disk capacity must remain free after the backup files are copied back to ensure operational stability.
Before initiating a restore, PBM performs a comprehensive disk space evaluation on every mongod instance. This includes:
- Total disk size
- Used and available disk space
- Estimated size available for PBM operations. It is calculated as
85% of the total size - used space - Backup size. The backup size must be less than the estimated size available for PBM operations. PBM uses the uncompressed backup size for evaluation. This information is stored in the backup metadata and is available in the
pbm describe-backupcommand output.
Note that point-in-time recovery oplog chunks are not evaluated. The remaining free space is considered sufficient for PBM to replay them successfully during the restore.
To illustrate this evaluation, consider the following example:
- Disk total: 10 GB
- Used: 6 GB
- Free space: 4 GB
- Available for PBM usage: 10GB * 85% - 6GB = 2.5 GB
The backup size must be less than 2.5 GB to proceed with the restore using the fallback directory.
PBM logs this evaluation in detail. You can view it using the pbm logs command.
If even one node in the cluster lacks sufficient disk space according to this calculation, PBM aborts the restore process.
Configuration¶
To configure physical restores with a fallback directory, use either the PBM configuration file or the command line:
Specify the following option in the PBM configuration file:
restore:
fallbackEnabled: true
You can start the restore with a fallback directory directly using the --fallback-enabled flag:
pbm restore --time <time> --fallback-enabled=true
A restore can succeed on most nodes, but it might fail on a few, resulting in a “partlyDone” status. You can configure PBM how to proceed with such partial restores:
restore:
allowPartlyDone: true
pbm restore --time <time> --fallback-enabled=true --allow-partly-done=true
If you allow partial restores (default value), PBM finalizes the restore. Once the cluster is up and running, the failed node receives the necessary data from other members through an initial sync.
If you deny partial restores, PBM treats a cluster as unhealthy and falls it back to the original state. In this case you must have the restore.fallbackEnabled option set to true or run the pbm restore command with the --fallback-enabled flag. Otherwise, a restore won’t start.
Implementation specifics¶
- The use of fallback directory is supported for both replica set and sharded cluster deployments.
- The use of fallback directory is supported for both full physical and physical incremental backups
- You must have enough free space on every
mongodnode for PBM to copy thedbPathcontents to a fallback directory. After the file copy, at least 15% of the total disk size must remain free to ensure operational stability. This free space is also considered enough to replay oplog during point-in-time recovery. - In case of incremental backups, all increments are included in backup size calculation.
- You can only restore backups made with PBM version 2.10.0 using the fallback directory. For backups made with earlier PBM versions, PBM doesn’t have the uncompressed backup size and cannot evaluate the disk space for fallback directory. Therefore, PBM automatically disables the
fallbackEnabledsetting and logs this action.
Created: March 3, 2026