What’s new in Percona Everest 1.8.0¶
➡️ New to Percona Everest? Get started with our Quickstart Guide.
Warning
Single Sign-On (SSO) authentication with Microsoft Entra ID does not function in Percona Everest 1.8.0. To ensure it functions properly, upgrade to version 1.8.1.
Expand to unleash the key updates
📋 Release summary¶
| # | Category | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Release highlight: Dataimporters in Percona Everest | Import external database backups directly into clusters managed by Percona Everest |
| 2. | New features | Check out the new features introduced in Percona Everest 1.8.0 |
| 3. | Improvements | Discover all the enhancements featured in Percona Everest 1.8.0 |
| 4. | Bug fixes | Find out about all the bugs fixed in Percona Everest 1.8.0 |
| 5. | Known limitations | Discover all the known limitations in Percona Everest 1.8.0 |
🌟 Release highlights¶
Import external backups into Percona Everest clusters¶
Technical Preview
The external backup import feature in Percona Everest is currently in Technical Preview. Early adopters are advised to use this feature only for testing purposes and not in production environments.
Starting with Percona Everest 1.8.0, we are excited to roll out a new feature that allows you to directly import backups of clusters managed by the Percona Operators for MongoDB, MySQL (XtraDB), and PostgreSQL, into clusters managed by Percona Everest. This feature leverages an extensible framework that streamlines your backup process.
Key features¶
-
Import database backups of clusters managed by the Percona Operators for MongoDB, MySQL (XtraDB), and PostgreSQL into database clusters managed by Percona Everest.
-
Customize the import process using tools like
mongodump,pg_dump, ormysqldump. -
A pluggable and extensible framework that can adapt to various import needs and workflows.
How to import external database backups using the Percona Everest UI¶
Here are the steps to import the external backups:
-
Navigate to the Percona Everest homepage and click Import.
-
Select the database type you want to import (MySQL, PostgreSQL, or MongoDB). The Basic information page will be displayed.
-
Fill in the details on the Basic information page and click Continue. This will take you to the Import information page.
-
On the Import Information page, enter the following:
-
Choose the data importer from the dropdown.
-
Provide S3 details.
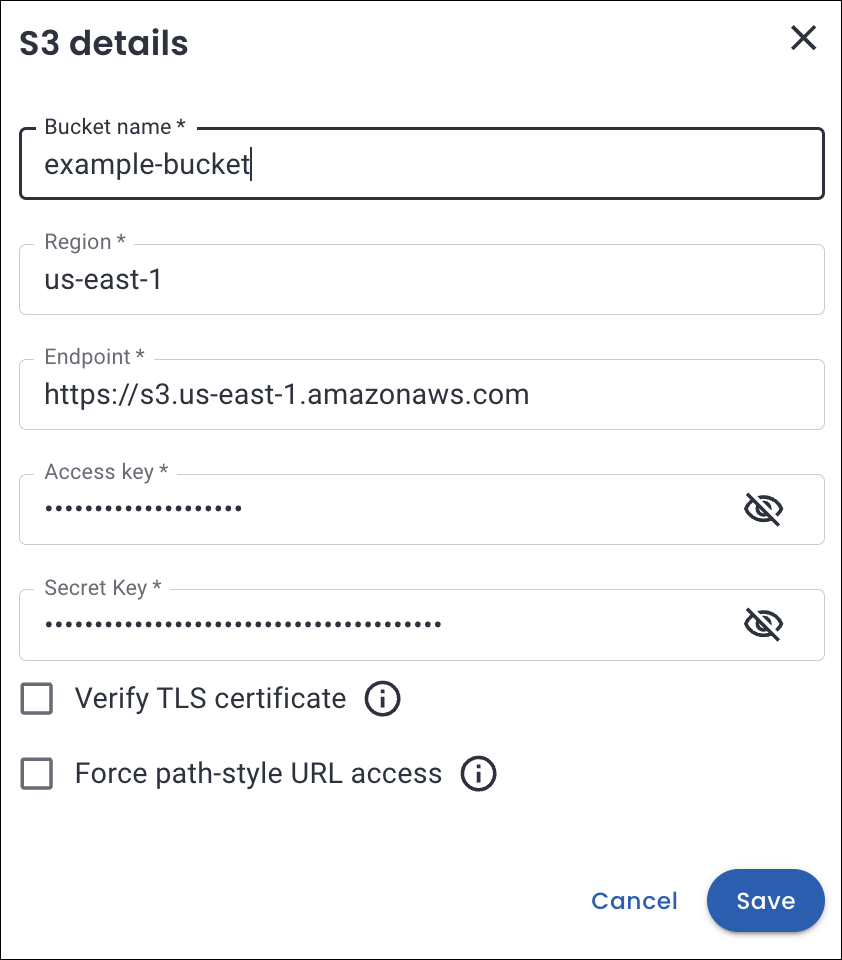
-
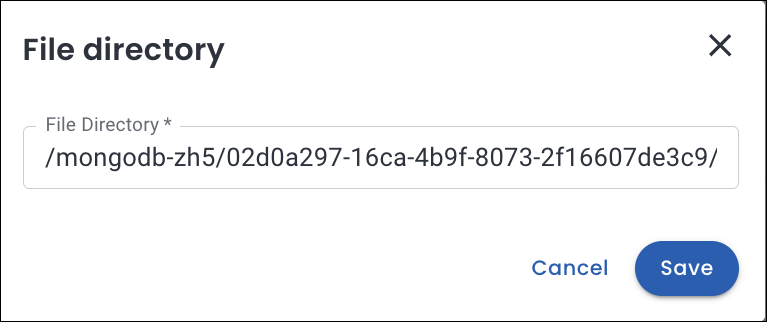
Specify the File Directory path within your S3 bucket where the backup files are stored. Click Save.
Refer to the documentation for details on the correct file path format.
-
Enter the key-value pairs of the user secrets (For MongoDB and MySQL) in the DB credentials section.
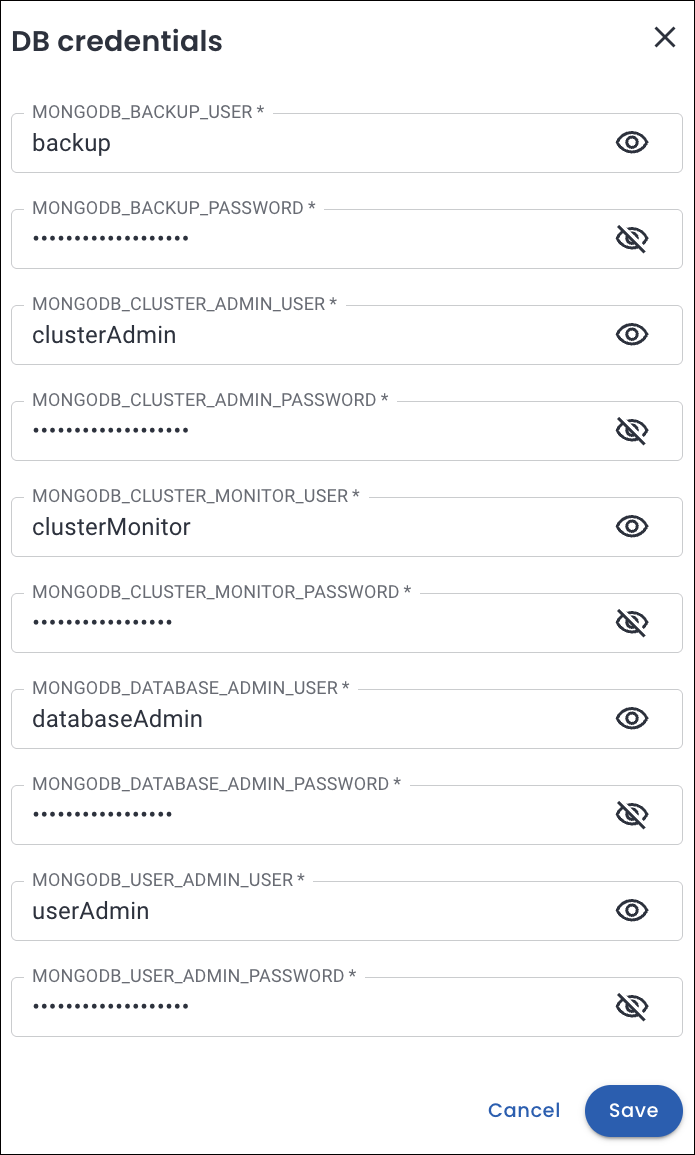
-
-
Click Continue until you reach the end of the wizard. Once the import is successful, the database status will change to Up.
If you’re looking to dive deeper into this feature, don’t miss out on our comprehensive documentation.
New features¶
-
EVEREST-2068, EVEREST-2069, EVEREST-2070: Starting with Percona Everest 1.8.0, you can import external backups created using the Percona Operators for PostgreSQL, MySQL, and MongoDB into clusters managed by Percona Everest.
While the default DataImporters are designed explicitly for backups compatible with Percona Operators, the DataImporters framework is flexible and extensible. This allows you to customize your import process using any backup and restore tools you prefer, such as
pg_dump,mysqldump,mongodump, and others.
Improvements¶
-
EVEREST-1806: We have improved the visibility of the proxy validation message when creating a MySQL database.
-
EVEREST-1909: Duplicate IP/Netmask entries for external access are now prevented, ensuring accurate network configurations in database clusters.
-
EVEREST-1946: Since disk resizing is an irreversible operation, Percona Everest now prompts for confirmation before applying disk size changes.
-
EVEREST-1958: When you revisit a wizard step, Percona Everest now automatically expands any collapsed section that contains fields with validation errors. This enhances usability by ensuring errors are immediately visible and easier to resolve.
-
EVEREST-1964: The Edit action in the upgrade section has been renamed to Upgrade to better reflect its purpose, as upgrading is the only supported action in that context.
-
EVEREST-2002: In the Helm upgrade flow, Percona Everest now performs a pre-check to validate CRD compatibility before proceeding with the upgrade. This helps prevent cluster breakage by ensuring that all required Custom Resource Definitions are present and compatible, improving upgrade reliability.
-
EVEREST-2003: The expandable section in the Database Overview page has been removed for an enhanced UX.
-
EVEREST-2005: We’ve added a View DB status Details option to the Actions menu on the Overview page, providing quicker access to database status and cluster-specific information.
Bug fixes¶
-
EVEREST-1838: The Edit option for Point-in-Time Recovery (PITR) was incorrectly disabled for MySQL and MongoDB clusters, even when PITR was enabled. This issue has now been resolved.
-
EVEREST-1890: During MySQL database cluster creation, the selected number of proxies was incorrectly reset to 1 in the UI. The proxy count now reflects the user’s selection accurately.
-
EVEREST-1895: Resolved an issue where the Point-in-Time Recovery (PITR) time could not be adjusted from the last successful backup. Users can now modify the PITR time as intended.
-
EVEREST-1948: The component Age was previously displayed incorrectly on the Components tab. It now reflects the accurate age of each component.
-
EVEREST-2001: Addressed an issue where the Disk, CPU, and Memory input fields became unresponsive or difficult to edit when large values were entered. Input behavior is now consistent and reliable across all value ranges.
-
EVEREST-2030: Fixed an issue where users were not logged out after account deletion. The UI remained active even though the API token had been invalidated. The session is now properly terminated upon deletion.
-
EVEREST-2037: Fixed an issue where the
Policy is being usedmessage appeared even when the policy was not linked to any database. -
EVEREST-2043: While running
everestctl install, settingpmm.enabled=truecaused PMM to be deployed in the default namespace instead of theeverest-systemnamespace. PMM is now correctly deployed in theeverest-systemnamespace, ensuring consistency withhelm install. -
EVEREST-2052: The PMM client was terminated due to out-of-memory (OOM) errors under specific workloads. This issue has now been resolved.
Known limitations¶
Helm upgrade requirement for Percona Everest 1.8.0¶
- To upgrade from Percona Everest 1.8.0, you have to use the
--take-ownershipflag, which is available only in Helm CLI v3.17.0 or later. If you need to upgrade with an older version of the Helm CLI, the upgrade may fail due to CRD ownership validation errors. However, you can manually add the required labels and annotations to the Percona Everest CRDs to avoid this issue. For detailed steps on this process, refer to our documentation.
Limitations for DataImporters¶
-
Importing backups into sharded MongoDB clusters is currently not supported. The
DataImporterfor MongoDB only works with non-sharded clusters. -
Percona Everest does not validate file paths or verify the existence of files in the specified storage buckets. Make sure that the backup directory path is correct and accessible.
-
For some data import methods, you must provide database user credentials that match those of the source database. Percona Everest does not validate these credentials, so ensure they are accurate.
-
Percona Everest does not verify the compatibility of imported data with the version of the target DatabaseCluster. Ensure that the backup is compatible with the database version managed by Percona Everest.
🚀 Ready to Upgrade?¶
Upgrade to Percona Everest 1.8.0 to access these new features and improvements.
📖 Explore our Upgrade section for the upgrade steps.