📦 What’s new in Percona Everest 1.7.0¶
➡️ New to Percona Everest? Get started with our Quickstart Guide.
Before you upgrade
-
Before upgrading to Percona Everest 1.7.0, run the following command:
For details, refer to the Known limitations section.kubectl label namespaces everest-system app.kubernetes.io/managed-by- -
Single Sign-On (SSO) authentication with Microsoft Entra ID does not function in Percona Everest 1.7.0. To ensure it functions properly, upgrade to version 1.8.1.
🔑 Expand to unleash the key updates
| # | Release summary | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | GKE Autopilot clusters | Deploy Percona Everest on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) Autopilot clusters |
| 2. | Pod Scheduling policies | Pod Scheduling for optimized Kubernetes scheduling¶ |
| 3. | TLS support | Improved Security with TLS support |
| 4. | Operator Upgrades | Support for Percona XtraDB Cluster (PXC) operator |
| 5. | Breaking Changes | Learn about the breaking changes introduced in Percona Everest 1.7.0 |
| 6. | New features | Check out the new features introduced in Percona Everest 1.7.0 |
| 7. | Improvements | Discover all the enhancements featured in Percona Everest 1.7.0 |
| 8. | Bugs | Find out about all the bugs fixed in Percona Everest 1.7.0 |
| 9. | Known limitations | Discover all the known limitations in Percona Everest 1.7.0 |
🌟 Release highlights¶
Deploy Percona Everest on GKE Autopilot¶
You can now install Percona Everest on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) Autopilot clusters. GKE Autopilot provides a fully managed Kubernetes environment, where Google automatically handles node provisioning, scaling, and security.
📚 Learn more about GKE Autopilot in the official documentation.
Pod scheduling policies in Percona Everest¶
We are thrilled to introduce Pod scheduling policies for Percona Everest. This feature allows database administrators to manage database workload scheduling on Kubernetes. These policies enhance system resilience and ensure that your resources are utilized to their fullest potential.
The Pod scheduling policy is preset that includes a set of Kubernetes Affinity rules applied to the appropriate DB cluster components.
Kubernetes features three primary types of affinity that play a crucial role in how pods are scheduled and interact within a DB cluster:
-
Pod affinity: Co-locates pods on the same node or topology domain.
-
Pod anti-affinity: Ensures pods are scheduled on different nodes or domains.
-
Node affinity: Schedules pods based on node labels and conditions.
Default configuration for Pod scheduling policies¶
In Percona Everest, the default pod scheduling policies are preset rules that help ensure the optimal placement of database components across a Kubernetes cluster. These predefined Pod scheduling policies come bundled with every Percona Everest deployment. Thus, Percona Everest users can utilize these predefined settings without the need to create custom rules for every database cluster they set up.
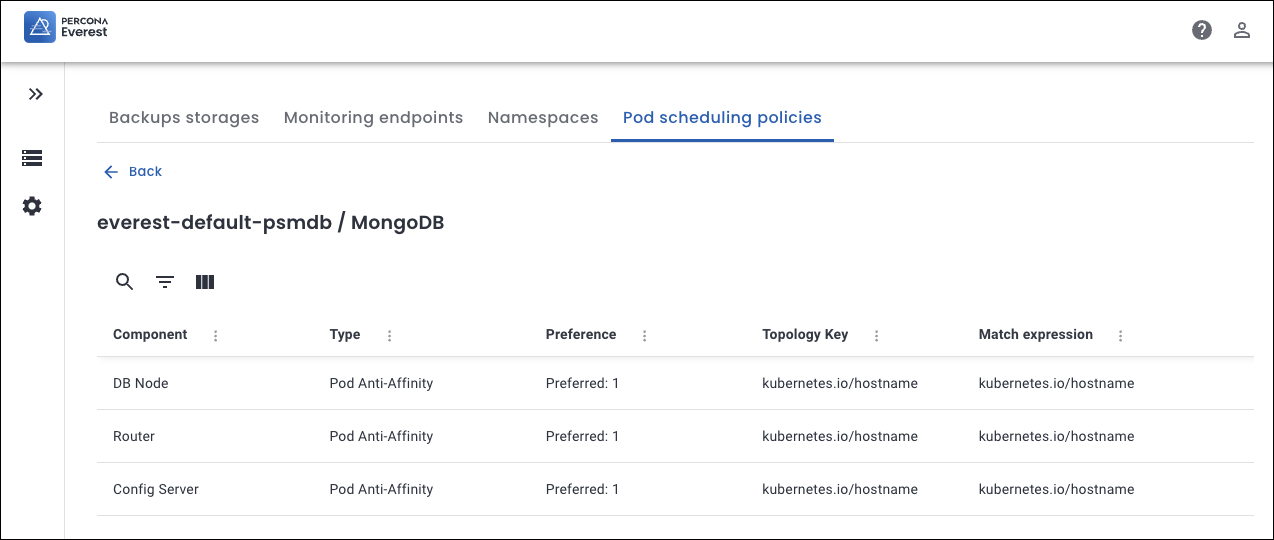
📘 To dive deep into this topic, see our documentation.
Custom Pod scheduling policies¶
If you need more control, you can define custom Pod scheduling policies to manage how database pods are placed across Kubernetes nodes. These policies offer fine-grained control over pod distribution using Kubernetes affinity and anti-affinity rules.
To create a custom policy, configure the scheduling rules via the Everest UI, as shown below:
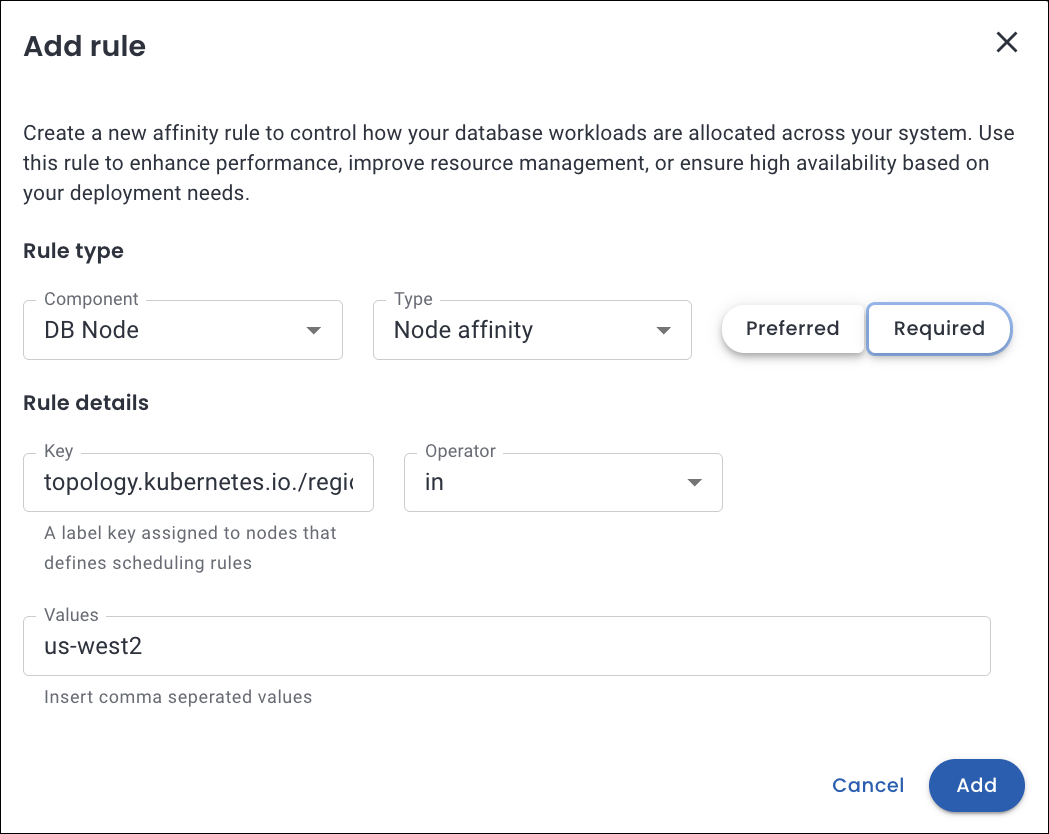
📘 To explore this topic in detail, see our documentation.
Improved Security with TLS support¶
Starting with version 1.7.0, Percona Everest can be set up to use Transport Layer Security (TLS) for all incoming connections to the Everest API server. TLS encrypts communication between clients and the API server, safeguarding data from interception or tampering.
Administrators can configure server certificates and private keys to enable secure HTTPS access. This enhances the overall security of production environments.
📘 To explore this topic in detail, see our documentation.
Support for Percona XtraDB Cluster (PXC) operator 1.17.0¶
Percona Everest 1.7.0 now includes support for PXC Operator version 1.17.0.
🛑 Breaking changes¶
Pod scheduling policy migration for GitOps users¶
With the introduction of Pod scheduling policies in Percona Everest 1.7.0, a new field named podSchedulingPolicyName has been added to the spec section of the DatabaseCluster CRD.
During the upgrade process to Percona Everest 1.7.0, we run a migration script to apply the default scheduling policies to existing DB clusters. However, if you are using GitOps to manage your Percona Everest deployment, you must manually add the podSchedulingPolicyName field to your DatabaseCluster CR manifests to ensure that the default scheduling policies are applied correctly.
The default pod scheduling policies are predefined for each database engine and are as follows:
- MySQL:
everest-default-mysql - MongoDB:
everest-default-mongodb - PostgreSQL:
everest-default-postgresql
Example: MySQL DatabaseCluster CR manifest
Here’s an example of DatabaseCluster CR manifest with the podSchedulingPolicyName field:
apiVersion: everest.percona.com/v1alpha1
kind: DatabaseCluster
metadata:
name: my-database-cluster
spec:
podSchedulingPolicyName: everest-default-mysql # Specify the default MySQL scheduling policy
engine:
type: pxc
# Other fields...
OIDC integration with Microsoft Entra ID¶
If you are using Microsoft Entra ID as your OIDC provider for Percona Everest, please be aware of a breaking change in the way access tokens are validated.
The access tokens issued by Microsoft Entra ID must now include the aud claim with the value set to the correct application identifier. This can be achieved by requesting the <your-app-client-id>/.default scope when obtaining the access token.
Ensure that you configure Everest’s OIDC settings requesting the correct scope to avoid any disruptions in your authentication flow:
everestctl settings oidc configure \
--issuer-url=http://url.com \
--client-id=<your-app-client-id> \
--scopes=openid,profile,email,<your-app-client-id>/.default
📘 For detailed information, see our documentation.
New Features¶
-
EVEREST-1605: We’ve introduced a Pod Scheduling Policy panel in the Advanced Configuration step of the DB cluster creation wizard.
This feature allows you to define custom Affinity rules while creating a new DB cluster, providing greater control over pod placement and workload distribution.
-
EVEREST-1606: You can now apply Affinity rules to existing DB clusters via a new Pod Scheduling Policy panel, which is available in the Advanced Configuration section of the DB cluster overview page.
- This feature allows users to enable the Pod Scheduling Policy for an individual DB cluster after its creation.
- Once enabled, users can select one of the predefined scheduling policies to influence pod placement according to their workload distribution or fault-tolerance needs.
-
EVEREST-1607: Database administrators can now quickly view the current affinity configuration status directly from the DB Overview tab. Additionally, a direct navigation link to the Affinity section in the Components tab has been added, allowing administrators to access and modify Kubernetes affinity rules for the database components.
-
EVEREST-1862: The Components tab now features a new Topology View to improve the visibility and management of DB clusters deployed in Percona Everest. This interactive view visually represents the components of the cluster, including pods, services, status, and their relationships.
-
EVEREST-1987: We have added support for PXC operator v1.17.0.
-
EVEREST-1998 Database administrators now have increased control over creating, updating, and deleting Pod Scheduling Policies. This improvement simplifies workload distribution in Percona Everest. Also, it helps to optimize resource utilization and efficiency, ensuring smoother operations and improved scheduling.
Improvements¶
-
EVEREST-1106: Percona Everest administrators can now delete users created with
everestctl. Once a user is removed, they can no longer use their access tokens to make requests to the Everest API. This improves security by preventing unauthorized access by former users and allows for better user permission management within Percona Everest. -
EVEREST-1180: Percona Everest can now be configured to use Transport Layer Security (TLS) for all incoming connections to the Everest API server.
-
EVEREST-1901: When adding a Backup Bucket, trailing spaces at the end of the bucket name prevented it from being added. This issue often occurred when copying names, which caused confusion. We have resolved this by removing trailing spaces.
-
EVEREST-1902: When adding Monitoring Endpoint URLs, trailing spaces at the end of the URL prevented them from being added. This issue often occurred when copying URLs, leading to confusion. We have improved this by trimming trailing spaces.
-
EVEREST-1974: The Storage Class field was previously non-editable when modifying a DB cluster in the Percona Everest UI, but the message stated that it could be changed based on performance needs. The UI now clearly shows that the Storage Class can only be selected during cluster creation.
-
EVEREST-1914: Focus state is now correctly removed when users click outside of an input field on the UI. This enhances usability by ensuring that input fields no longer appear active after focus is lost.
-
EVEREST-1923: The Everest API access token now becomes invalid immediately upon logout, preventing unauthorized access to your account.
-
EVEREST-1931: We have improved the diagram view for the default zoom and search functionality of DB cluster components in the following ways:
- Default Zoom Level: A predefined zoom level is now set to ensure all components are visible upon loading.
- Reset View Button: This button allows you to reset the zoom level and reposition the view to its default settings.
- Search Functionality: A search bar has been added to the diagram view, similar to the one in the table view, making it easier to locate components.
Bug Fixes¶
-
EVEREST-1623: We have resolved an issue where HAProxy kept restarting in a 5-node MySQL cluster, which caused connection instability and made the database unavailable.
-
EVEREST-1651: Fixed a problem where creating a new MySQL database from a backup would fail if the database name exceeded a certain length.
-
EVEREST-1700: Fixed an issue where enabling PMM monitoring led to multiple unnecessary reconciliation cycles and pod restarts during database cluster creation, significantly slowing down startup times. A similar issue that occurred during cluster deletion, causing pod restarts before termination, has also been resolved.
-
EVEREST-1754: Fixed an issue where the error message storage is (re)initializing was displayed on the UI intermittently.
-
EVEREST-1785: Resolved an issue with the PITR pod for a one-node MySQL database that restarted multiple times.
-
EVEREST-2011: The restore function for the MySQL database is now working correctly in PXC version 1.17.0.
-
EVEREST-2018: The TLS installation instructions now accurately guide users on accessing the user interface (UI).
-
EVEREST-1891: When trying to create a database from a backup with the same name as an existing database, there was no validation message or warning. The Continue button became unresponsive and did not provide any error message to the user. We have now resolved this issue.
-
EVEREST-1984: Resolved an issue where creating multiple backup schedules in PostgreSQL led to an error.
-
EVEREST-2025: Resolved an issue where the Content-Security-Policy header included an invalid
connect-srcvalue if the OIDC issuer URL ended with a trailing slash. The policy is now correctly generated.Thanks to @aurimasniekis for reporting and fixing this issue.
-
EVEREST-343: Resolved an issue that caused Percona Everest installation to fail on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) Autopilot clusters.
Known limitations¶
Upgrade to v1.7.0 fails with Namespace error¶
If you installed Percona Everest version prior to 1.4.0 and successively upgraded to version 1.6.0, you may run into issues when upgrading to version 1.7.0.
Workaround
Run the following command before you upgrade to Percona Everest version 1.7.0:
kubectl label namespaces everest-system app.kubernetes.io/managed-
Microsoft Entra ID¶
When integrating Microsoft Entra ID as your OIDC provider for Percona Everest, it’s essential to ensure that the access tokens issued are compatible with Percona Everest’s token validation logic.
📘 For detailed information, see our documentation.
🚀 Upgrade now¶
Upgrade to Percona Everest 1.7.0 to access these new features and improvements.
📘 Explore our Upgrade section for the upgrade steps.