LDAP authorization¶
LDAP authorization allows you to control user access and operations in your database environment using the centralized user management storage – an LDAP server. You create and manage user credentials and permission information in the LDAP server. In addition, you create roles in the admin database with the names that exactly match the LDAP group Distinguished Name. These roles define what privileges the users who belong to the corresponding LDAP group.
Supported authentication mechanisms¶
LDAP authorization is compatible with the following authentication mechanisms:
Authentication and authorization with direct binding to LDAP¶
You can configure Percona Server for MongoDB to communicate with the LDAP server directly to authenticate and authorize users.
The advantage of using this mechanism is that it is easy to setup and does not require pre-creating users in the dummy $external database. Nevertheless, the --authenticationDatabase connection argument will still need to be specified as $external.
The following example illustrates the connection to Percona Server for MongoDB from the mongosh shell:
mongosh -u "CN=alice,CN=Users,DC=engineering,DC=example,DC=com" -p --authenticationDatabase '$external' --authenticationMechanism PLAIN
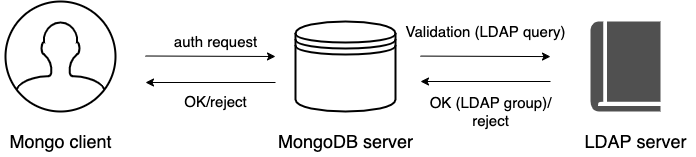
The following diagram illustrates the authentication and authorization flow:
-
A user connects to the database providing their credentials
-
If required, Percona Server for MongoDB transforms the username to match the user in the LDAP server according to the mapping rules specified for the
--ldapUserToDNMappingparameter. -
Percona Server for MongoDB queries the LDAP server for the user identity and/or the LDAP groups this user belongs to.
-
The LDAP server evaluates the query and if a user exists, returns their LDAP groups.
-
Percona Server for MongoDB authorizes the user by mapping the DN of the returned groups against the roles assigned to the user in the
admindatabase. If a user belongs to several groups they receive permissions associated with every group.
Username transformation¶
If clients connect to Percona Server for MongoDB with usernames that are not LDAP DN, these usernames must be transformed to the format acceptable by LDAP.
To achieve this, the --ldapUserToDNMapping parameter is available in Percona Server for MongoDB configuration.
The --ldapUserToDNMapping parameter is a JSON string representing an ordered array of rules expressed as JSON documents. Each document provides a regex pattern (match field) to match against a provided username. If that pattern matches, there are two ways to continue:
-
If there is the
substitutionvalue, then the matched pattern becomes the username of the user for further processing. -
If there is the
ldapQueryvalue, the matched pattern is sent to the LDAP server and the result of that LDAP query becomes the DN of the user for further processing.
Both substitution and ldapQuery should contain placeholders to insert parts of the original username – those placeholders are replaced with regular expression submatches found on the match stage.
So having an array of documents, Percona Server for MongoDB tries to match each document against the provided name and if it matches, the name is replaced either with the substitution string or with the result of the LDAP query.
Escaping special characters in usernames¶
A username can contain special characters in any of its parts. A special character is any character which is not alphanumeric or not an ASCII character.
These characters must be escaped to formulate the correct LDAP query on the following stages:
- To transform a username to the LDAP DN, and the matched pattern of a username must be first queried in the LDAP server to become the DN.
- To retrieve the groups a user is the member of.
Additionally, the username pattern to match for the transformation can have special characters that must be escaped too.
What exactly characters require escaping depends on the Percona Server for MongoDB configuration. Namely, on the configuration of the LDAP query template and the regular expressions inside the --ldapUserToDNMapping parameter.
The escaping rules are described in the following documents:
- RFC 4514 | LDAP: Distinguished Names - Escaping in Distinguished Names
- RFC 4515 | LDAP: String Representation of Search Filters - LDAP search filters utilize its own escaping mechanism
- RFC 4516 | LDAP: Uniform Resource Locator - General URL escaping rules.
Their explanation is out of the scope of the Percona Server For MongoDB documentation. Please review the RFC directly or use your preferred LDAP resource.
To summarize, username escaping happens in the following cases:
- When a username is defined as the LDAP DN and has special characters in any of its parts.
- When a username must be transformed to the LDAP DN and the username pattern for the transformation has special characters
- When the transformed LDAP DN value contains special characters in any of its parts.
LDAP referrals¶
As of version 6.0.2-1, Percona Server for MongoDB supports LDAP referrals as defined in RFC 4511 4.1.10. For security reasons, referrals are disabled by default. Double-check that using referrals is safe before enabling them.
To enable LDAP referrals, set the ldapFollowReferrals server parameter to true using the setParameter command or by editing the configuration file.
setParameter:
ldapFollowReferrals: true
Connection pool¶
As of version 6.0.2-1, Percona Server for MongoDB always uses a connection pool to LDAP server to process bind requests. The connection pool is enabled by default. The default connection pool size is 2 connections.
You can change the connection pool size either at the server startup or dynamically by specifying the value for the ldapConnectionPoolSizePerHost server parameter.
For example, to set the number of connections in the pool to 5, use the setParameter command:
db.adminCommand( { setParameter: 1, ldapConnectionPoolSizePerHost: 5 } )
setParameter:
ldapConnectionPoolSizePerHost: 5
Support for multiple LDAP servers¶
As of version 6.0.2-1, you can specify multiple LDAP servers for failover. Percona Server for MongoDB sends bind requests to the first server defined in the list. When this server is down or unavailable, it sends requests to the next server and so on. Note that Percona Server for MongoDB keeps sending requests to this server even after the unavailable server recovers.
Specify the LDAP servers as a comma-separated list in the format <host>:<port> for the –ldapServers option.
You can define the option value at the server startup by editing the configuration file.
security:
authorization: "enabled"
ldap:
servers: "ldap1.example.net,ldap2.example.net"
You can change ldapServers dynamically at runtime using the setParameter.
db.adminCommand( { setParameter: 1, ldapServers:"localhost,ldap1.example.net,ldap2.example.net"} )
{ "was" : "ldap1.example.net,ldap2.example.net", "ok" : 1 }
See also
MongoDB Documentation:
Configuration¶
For how to configure LDAP authorization with the native LDAP authentication, see Setting up LDAP authentication and authorization using NativeLDAP.